

A ball is thrown vertically upwards with a velocity of 20 m/s. A car attains 54 km/h in 20 s after it starts. Calculate the acceleration of the car.Īns. Two seconds thereafter it is moving at 60 km/h. Initial velocity = +v 0 (in upward directions)ĭisplacement = –h (in downward direction) Let initial velocity is v 0 which is in vertically upward direction and finally comes down to the ground as shown in figure. Motional quantities, which are in downward-direction, are taken as negative. Motional quantities in upward-direction are taken as positive. To solve such types of problem, the following sign convention is used:. When an object is thrown in space in such a way that at first it goes up and then comes down. When an object is thrown in a downward direction (taking positive) in space with initial velocity v0.Īcceleration = +g (in downward direction) When an object is thrown in upward direction (taking positive) in space with initial velocity v0.Īcceleration = –g (in downward direction) In a real experiment air resistance cannot be neglected. When an object is thrown upward or downward, in both cases same acceleration ‘g’ will be experienced by the object, which acts in downward direction. Here acceleration will be acceleration due to gravity. So equations of motion for uniformly accelerated motion can be used which are Motion under gravity is a uniformly accelerated motion. Motion under gravity means an object is in motion in space under the force of gravity alone.
Find area of rectangle 3rd grader free#
Motion of body is called free fall if only force acting on it is gravity (i.e. If a body moves with uniform velocity, its acceleration is zero i.e. If a body comes to rest, its final velocity v = 0 or, if a body reached the highest point after being thrown upwards its final velocity v = 0 but has acceleration (acting). If a body starts from rest its initial velocity u = 0. If a body is dropped from a height then its initial velocity u = 0 but has acceleration (acting). The distance covered by the body in nth second will be. [distance covered by a body along a straight line in n second. S = ut + 1/2 at 2 is the distance covered by a body in t s.
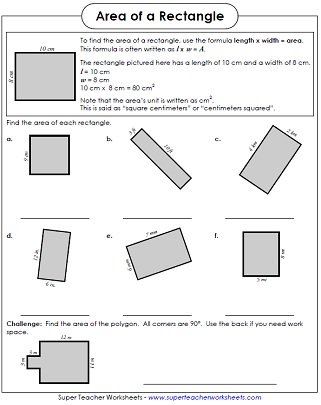
Putting this value of ‘t’ in equation …(i) Distance traveled = Average velocity × timeįrom the second equation of motion we have, The distance traveled by moving body in time ‘t’ is ‘S’ then the average velocity = (v + u)/2. Suppose a body has an initial velocity ‘u’ and uniform acceleration ‘a’ for time ‘t’ so that its final velocity becomes ‘v’. This equation is known as the first equation of motion. Suppose it is subjected to a uniform acceleration ‘a’ so that after time ‘t’ its final velocity becomes ‘v’. Third Equation of motion : v 2 - u 2 = 2asĬonsider a body having initial velocity ‘u’.Second Equation of motion : s = ut + 1/2at 2.These equations are called equations of motion. Nets can be used to find the area of 3 dimensional shapes.When the body is moving along a straight line with uniform acceleration, a relation can be established between velocity of the body, acceleration of the body and the distance travelled by the body in a specific time by a set of equations. A net is a pattern made when the surface of a three-dimensional figure is laid out flat showing each face of the figure.Then the formula for calculating the area of a regular hexagon would be –Īrea of a Hexagon = $\frac$ x (Sum of parallel sides) x (Distance between parallel sides) Let one side of a regular hexagon be “s”. The area of a regular hexagon can be calculated if we know one side of the hexagon. Find out the areas of these shapes by counting the number of squares they cover. Let us understand the area with an example. For example, the area, of the following are usually measured as under – The unit for measuring the area depends on the size of the area being used.
Find area of rectangle 3rd grader how to#
Mi – mi 2 (1 mi 2 is equal to 1 square miles) How to choose the correct unit when representing the area of a shape? Km – km 2 (1 km 2 is equal to 1 square kilometres) M – m 2 (1 m 2 is equal to 1 square metres) Mm – mm 2 (1 mm 2 is equal to 1 square millimetres)Ĭm – cm 2 (1 cm 2 is equal to 1 square centimetres) Let us see who the different units are used to represent the area of a surface. Hence, the unit of area is a unit square. to measure a region we use a square as a unit.
The units used to measure area are based on the units of length, i.e.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
